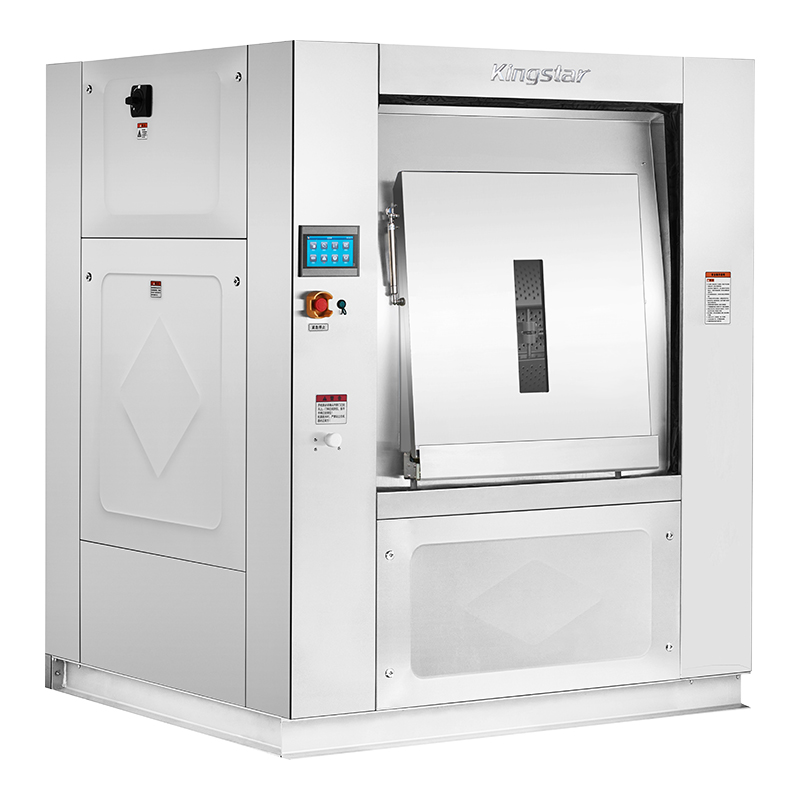
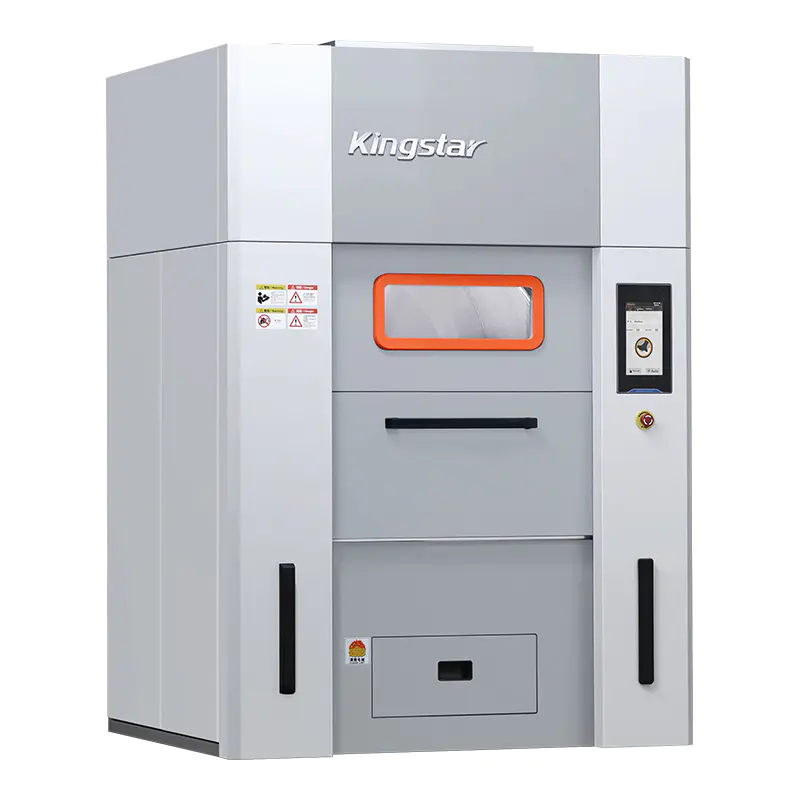
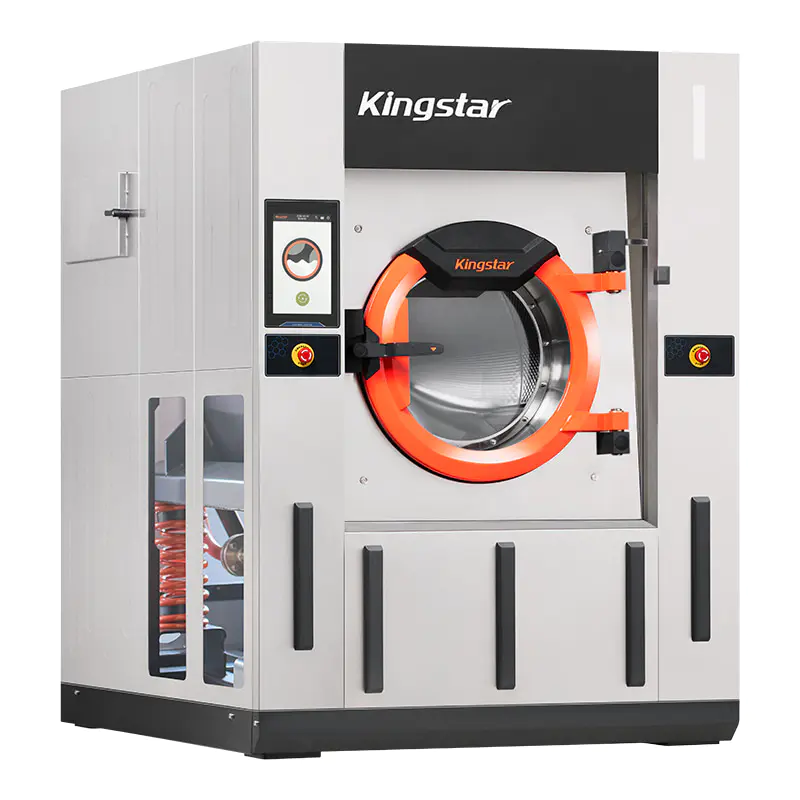
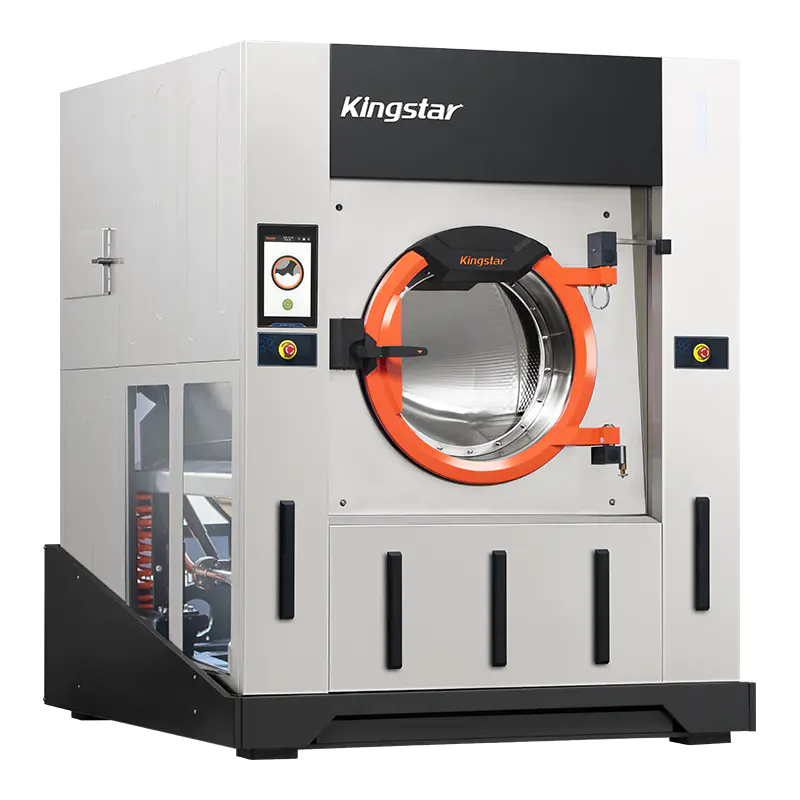
Barrier Washer(50/70/100kg)
Designed to meet the stringent standards of cleanroom environments, this advanced washer-extractor features a dual-compartment isolation system that ensures complete separation of clean and contaminated zones. Engineered specifically for cleanroom laundries, it delivers reliable cleanliness for anti-static garments, cleanroom gloves, and lint-free wipes.Beyond cleanroom applications, it also excels in handling high-contamination and high-pathogen laundry such as hospital bed linens, surgical gowns, and infectious department textiles, offering unparalleled hygiene and safety.
This makes it the ideal choice for microelectronics, semiconductors, optoelectronics, biotechnology, and pharmaceutical industries — and especially for medical institutions seeking a professional-grade cleanroom laundry solution.
-

Laundry
-

Dry cleaner
-

Self-service
laundry
- 50kg
- 70kg
- 100kg
(86)+86-13917089379
-

① Shock Absorption Design
The machine adopts an underhung shock absorption structure. Equipped with German-imported air springs and hydraulic dampers, it operates with low vibration and low noise, making it suitable for cleanroom environments. -

② Detergent Dispensing Design
Utilizes peristaltic pumps to automatically dispense liquid detergents with high precision. -

③ Safety Door Lock Design
The door is made of 304 stainless steel and equipped with a safety lock and interlock control system. This system provides reliable safety protection: the door cannot be opened while the machine is running, and the machine cannot start if the door is not properly closed. Additionally, when one side door is open, the other side remains locked to ensure isolation. -

④ Stable, Efficient, and Long Service Life Design
The washing drum is horizontally mounted and supported by double-side bearings, ensuring smooth operation and high dewatering performance. The overall machine is designed for a long service life. -

⑤ 40 Wash Programs
Equipped with a full-color LCD touchscreen, the system features a menu-based interface and human-machine interaction mode with three-level user access. It supports up to 40 customizable wash programs. A programmable logic controller (PLC) is standard for pharmaceutical industry users. -

⑥ Dual-Door Design (Front and Rear)
The front and unloading from the rear. When installed through a partition wall, it effectively separates the washing area (soiled side) from the finishing area (clean side). Loading and maintenance are performed in the washing area, while unloading and packaging are done in the finishing area, effectively preventing cross-contamination. -

⑦ 304 Stainless Steel Construction
All components that come into contact with water—such as the inner drum, outer tub, outer door, inlet valve, drain valve, and heating elements—are made of high-quality 304 stainless steel. This provides excellent resistance to acids and alkalis, superior corrosion protection, and prevents metal rust. -

⑧ Recessed Drum Design
The washing drum features a recessed-hole design that undergoes both manual grinding and electrolytic polishing, ensuring a smooth surface that won't snag fabrics. A unique anti-leak baffle structure effectively prevents small items (such as lint-free wipes) from escaping during operation.
-
 Simple operation
Simple operation -
 Intelligentize
Intelligentize -
 Humanized design
Humanized design -
 High quality
High quality
|
Specification Model |
N2050 |
N2070 |
N2100 |
|
Water Consumption (L/cycle) |
650 |
860 |
1150 |
|
Compressed Air Consumption (m³/h) |
0.15 |
0.15 |
0.15 |
|
Compressed Air Pipe Diameter (mm) |
Φ8 |
Φ8 |
Φ8 |
|
Compressed Air Pressure (MPa) |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.6 |
|
Steam Consumption (kg/h) |
50 |
70 |
100 |
|
Water Inlet |
DN25 |
DN40 |
DN40 |
|
Steam Inlet |
DN25 |
DN25 |
DN25 |
|
Drain Outlet |
DN63 |
DN100 |
DN100 |
|
Recommended Capacity (kg) |
50 |
70 |
100 |
|
Power (kW) |
5.5 |
7.5 |
11 |
|
Inner Drum Size (mm) |
1064×570×506 |
1064×830×730 |
1220×860×1005 |
|
External Dimensions (mm) |
1390×1500×2140 |
1610×1500×2140 |
1720×1550×2265 |
|
Total Machine Weight (kg) |
2100 |
2650 |
3200 |
About us
Craftsman spirit, excellence, quality products are the bridge to the world!
Kingstar brand is the crown jewel of CLM in the commercial laundry industry. For over 20 years, we carefully selected and updated our material suppliers and technology. We aim to be the best in the industry internationally and offer more to clients who rely on us for their business.
We hold the leading status in the laundry manufacturing industry in China after 25+ years of experience.

Honor & Qualification
Choose comes from trust, and cooperation
comes from honesty.
NEWS
What is a barrier washer and how does it differ from a conventional washer?
Definition of a Barrier Washer
A barrier washer is a specialized type of industrial washing machine designed for environments where hygiene and contamination control are critical. Unlike conventional washers, which are freestanding units that open into a single space, barrier washers are installed through a physical wall, creating two distinct areas. One side of the machine is dedicated to loading soiled linen, and the opposite side is for unloading clean, sanitized linen. This structural separation ensures that dirty and clean textiles never cross paths, significantly reducing the risk of cross-contamination in sensitive industries such as healthcare, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and cleanroom facilities.
Definition of a Conventional Washer
A conventional washer is a standard washing machine used in domestic, commercial, or industrial settings that allows both loading and unloading from the same side. These machines are suitable for general laundry operations where contamination control is not a top priority. While they can effectively clean textiles through mechanical action, water, detergents, and heat, they do not provide the strict separation of clean and soiled zones required in industries with high hygiene standards. Conventional washers are commonly found in laundromats, hotels, restaurants, and residential settings.
Structural Differences Between Barrier and Conventional Washers
The most significant distinction between a barrier washer and a conventional washer lies in their structural design. Barrier washers are built into walls and have two doors, one on the soiled side and one on the clean side. This design enforces workflow segregation by physically separating the dirty loading area from the clean unloading area. In contrast, conventional washers have only one loading door, with both soiled and cleaned laundry handled from the same side. This design is suitable for environments where strict contamination prevention measures are not required but is insufficient in healthcare or laboratory applications.
Workflow and Process Separation
Barrier washers ensure that the laundry process follows a one-way workflow: dirty laundry is brought into the soiled area, washed inside the machine, and then retrieved only from the clean area. This one-directional movement of textiles minimizes contamination risks and supports compliance with hygiene regulations. Conventional washers, on the other hand, do not provide such segregation. Laundry is both loaded and unloaded from the same point, meaning staff must handle both dirty and clean textiles in the same space. This can increase the possibility of recontamination, particularly in settings where sterilization and cleanliness are essential.
Applications of Barrier Washers
Barrier washers are primarily used in industries and facilities that require strict infection control. These include hospitals, surgical centers, pharmaceutical plants, nursing homes, food production facilities, and cleanrooms. In these settings, the presence of bacteria, viruses, or other contaminants poses serious risks. By ensuring a strict separation between clean and dirty zones, barrier washers help maintain hygiene standards. Conventional washers, while versatile, are more suited for hotels, gyms, laundromats, and households, where the main requirement is efficient cleaning rather than sterile separation.
Hygiene and Contamination Control
Hygiene is the primary reason barrier washers differ from conventional washers. In healthcare environments, for example, contaminated linen can carry pathogens that must not come into contact with clean linen or the staff handling them. Barrier washers address this by acting as a physical barrier that eliminates crossover between the soiled and clean processes. Conventional washers lack this feature, so while they can wash laundry effectively, they cannot provide the same level of assurance against contamination. This makes barrier washers essential in infection-sensitive industries.
Installation Requirements
Barrier washers require a specific type of installation, typically involving the integration of the machine into a wall that divides the soiled and clean zones. This requires facility planning, as two separate rooms or zones must be created. The installation process ensures that one side is designated for dirty laundry input and the opposite side for sanitized output. Conventional washers are simpler to install because they do not require wall integration or separation of zones. They can be placed anywhere with proper water, drainage, and electrical connections, making them more versatile for general laundry needs.
Cost Considerations
The cost of barrier washers is generally higher than that of conventional washers due to their specialized design, installation requirements, and advanced features. They are considered long-term investments for facilities where hygiene is critical. The higher cost is justified by the reduced risks of cross-contamination and the compliance with strict regulations. Conventional washers are less expensive to purchase and install, making them more suitable for businesses or households with lower hygiene demands. The following table highlights the cost-related differences between the two types of washers:
| Washer Type | Initial Cost | Installation Complexity | Operational Expenses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barrier Washer | High | Requires structural integration | Moderate to High |
| Conventional Washer | Low to Moderate | Simple installation | Moderate |
Size and Capacity Options
Both barrier and conventional washers come in a range of sizes and capacities, but their target applications influence their design. Barrier washers are often designed in larger industrial capacities, as they are installed in healthcare facilities and industrial laundries that handle high volumes of textiles. Conventional washers, by contrast, are available in a wider range of sizes, from small household units to larger commercial models. This flexibility makes conventional washers suitable for diverse settings, while barrier washers remain specialized for high-volume, hygiene-sensitive environments.
Compliance with Industry Regulations
Barrier washers are designed to meet strict hygiene and infection control standards. In hospitals and pharmaceutical facilities, compliance with regulatory guidelines is essential, and barrier washers are specifically engineered to satisfy these requirements. They are often certified or compliant with healthcare infection control protocols, ensuring that facilities can meet legal and safety obligations. Conventional washers, while meeting general safety and efficiency standards, are not intended to meet the same rigorous hygiene regulations. This difference further defines their distinct roles in the laundry industry.
Operational Complexity
Operating a barrier washer involves a more structured process compared to conventional washers. Staff must follow strict protocols when handling soiled and clean linen, ensuring the workflow remains one-directional. Training is often required for staff working with barrier washers to maintain compliance with hygiene standards. Conventional washers, by contrast, are generally straightforward to use. Their operation is less complex, requiring basic knowledge of detergent dosing, cycle selection, and loading procedures. This makes them accessible to a wide range of users in different environments.
Maintenance and Durability
Barrier washers are engineered for heavy-duty use and long-term durability, as they are typically installed in facilities that handle large volumes of laundry daily. Their design includes robust components that withstand continuous cycles. Maintenance, however, can be more complex due to their integration into walls and the need to ensure hygiene standards are maintained. Conventional washers also offer durability but are designed for less demanding applications, depending on whether they are residential or commercial models. Their maintenance is generally simpler and less costly compared to barrier washers.
Energy and Water Consumption
Both barrier washers and conventional washers have evolved to include energy-efficient features. Barrier washers often integrate systems that optimize water levels and reduce chemical usage, which is especially important in industries aiming to reduce operational costs. Conventional washers also come with energy-saving features, but the primary focus is on general efficiency rather than compliance with strict operational protocols. The efficiency comparison between the two types of washers can be summarized as follows:
| Aspect | Barrier Washer | Conventional Washer |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High, optimized for hygiene protocols | Moderate to High depending on model |
| Energy Efficiency | Designed for long-term operational savings | Varies, household and commercial options available |
| Chemical Use | Optimized for reduced chemical consumption | Standard chemical dosing |
Industries That Rely on Barrier Washers
The industries that rely most heavily on barrier washers include healthcare, pharmaceuticals, food production, biotechnology, and research laboratories. In each of these industries, contamination poses significant risks, either to human health, product quality, or research integrity. The ability of barrier washers to maintain separation between soiled and clean textiles is crucial for minimizing these risks. Conventional washers, in contrast, are widely used in the hospitality industry, residential homes, gyms, and laundromats, where efficient cleaning is required but strict contamination control is unnecessary.
Advantages of Barrier Washers Over Conventional Washers
The advantages of barrier washers primarily relate to their ability to maintain hygiene. Their double-door design ensures separation between contaminated and clean textiles, reducing infection risks. They also help facilities meet regulatory compliance requirements. Conventional washers, while less specialized, are more affordable, easier to install, and more flexible in terms of location and application. Both washer types have advantages depending on the setting in which they are used, but barrier washers offer benefits that conventional washers cannot match in terms of infection control.
Challenges of Using Barrier Washers
Despite their benefits, barrier washers come with challenges. The initial investment is higher, installation is more complex, and maintenance requires skilled personnel. Facilities must also plan their workflows carefully, ensuring that staff are trained and protocols are strictly followed. Conventional washers do not pose these challenges and can be used with minimal setup and training. However, in environments where contamination control is essential, the additional challenges of barrier washers are outweighed by their ability to maintain hygiene.
Comparison Summary
The table below provides a summary comparison between barrier washers and conventional washers based on several critical factors:
| Factor | Barrier Washer | Conventional Washer |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Double door, wall-integrated | Single door, freestanding |
| Hygiene Control | High, prevents cross-contamination | Low, same area for dirty and clean |
| Installation | Complex, requires separate zones | Simple, flexible placement |
| Cost | High initial investment | Lower purchase cost |
| Industries Used | Healthcare, pharmaceutical, food processing | Hospitality, residential, laundromats |
| Workflow | One-way, controlled | Open, same side |
Future Trends in Washer Technology
The future of both barrier washers and conventional washers is influenced by technological advancements in automation, digital monitoring, and sustainability. Barrier washers are increasingly being integrated with automated systems that track load processing, hygiene compliance, and energy usage. Conventional washers are also evolving, with features such as smart connectivity, energy-efficient cycles, and enhanced user convenience. While their applications differ, both types of washers are expected to continue improving in terms of efficiency and usability, adapting to the specific demands of their industries.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch